London: An extinction event is any disastrous event that causes a rapid decrease in the bio diversity of the earth. It is believed that at least five such extinction events have occurred in the history of earth. The one such being 359 million years ago, which caused three-quarters of the species then, to wipe out from earth. Dinosaurs were one prominent species that said good bye to earth due to another extinction event.
Extinction event
There were controversies regarding the cause of these extinction events. The scientists from the University of Southampton claim that the exact cause of the extinction events has been found. They add to it that the situation is more alarming, for this cause is about to repeat, if the climate change on earth is not well addressed. Scientists call the extinction event that happened 360 million years ago ‘the Late Devonian Extinction’.
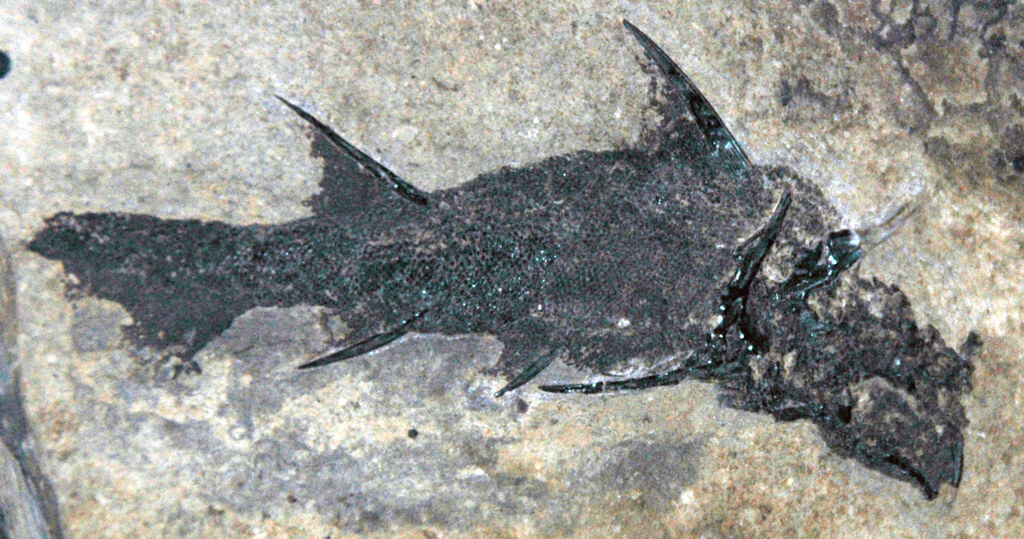

The scientists from University of Southampton claims that the cause of the Late Devonian Extinction was the break down of the Ozone layer, leading to an extra exposure of earth with harmful Ultra Violet (UV) rays. They collected rock samples from around the world, including Greenland, Bolivia and South America. In the lab they extracted ancient plant spores, which “had bizarrely formed spines on their surface”. This, according to them, was a direct result of DNA change or damage. Evidences are there which proves that this damage was caused due to uncontrolled UV ray exposure.
What causes Extinction event?
The ozone layer protects the earth from UV rays. One with basic high school knowledge knows that the ozone hole is formed due to chlorofluoro carbons in aerosol cans and dumped refrigerators. Ozone hole is prominent above the Antarctica region. The hole has begun to shrink in recent years after they were phased out. The factor that caused the Late Devonian extinction was definitely not aerosols. It was, according to the scientists, rising temperatures. Scientists find that the situation we are experiencing now, is exactly the same. Global temperature is rising. It is worsened when carbon fossil fuels are burnt uncontrollably.
The stratosphere is warm and humid just like the condition that persisted before the onset of Late Devonian. “This increased high-altitude water content then passes the threshold for an increased production of catalytically active (chlorine oxide) with ensuing increased rate of ozone loss,” the study said. “The recognition that a known extinction kill mechanism, the loss of the ozone layer, occurred not only during a large volcanic event, but at times of high global temperature identifies a new mechanism for mass extinctions. However, unlike an asteroid impact, higher temperatures are a certainty in the immediate future with implications for a similar collapse of the ozone layer”, says Prof. John Marshall, the lead scientist in the team.
“Current estimates suggest we will reach similar global temperatures to those of 360 million years ago, with the possibility that a similar collapse of the ozone layer could occur again, exposing surface and shallow sea life to deadly radiation. This would move us from the current state of climate change, to a climate emergency.”, another team member observed. The Late Devonian extinction was the second of five to hit Earth. Scientists in recent years have suggested we could be in the sixth right now. A UN report last year concluded a million species or more will go extinct in the next decade unless urgent action is taken. The detailed study is published in the journal Science and Advances.



![The Top & Most Popular Seafood Bucket Restaurants in Dubai for you [Never Miss]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/8-seafood-in-a-bucket-scaled-e1600739237403.jpg)
![Procedures for Renewing the Driving License in Abu Dhabi [3 Simple Steps]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Capture-9-e1595666454466.jpg)





