The Covid-19 test is a main factor that help to reduce the spread of this pandemic. But question arises, how accurate are the available Covid tests? The most common tests used to diagnose an infection with the novel corona virus are almost 100 percent effective if administered correctly. However, the same can’t be said of tests to determine if you’ve already had the disease and have developed antibodies.
Experts say diagnostic testing is one of the most powerful public health tools for fighting the spread of the corona virus. The tests identify people who may need treatment. Results also trace those who have been in contact with other individuals to help prevent the transmission of the disease further. This can assist epidemiologists in determining how widely the virus has spread.
There are two basic types of tests for the novel corona virus. One type diagnoses an infection and the other tests for antibodies.
Diagnostic test
Diagnostic tests detect active infections. This is the test you want if you think you’ve been exposed to the corona virus or are exhibiting symptoms of Covid-19. There are currently two types of diagnostic tests available.
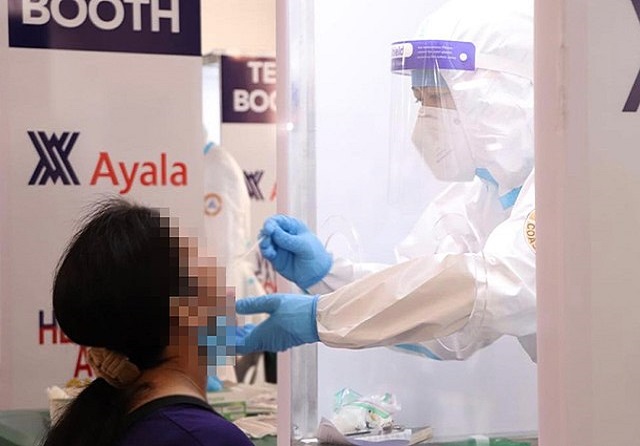
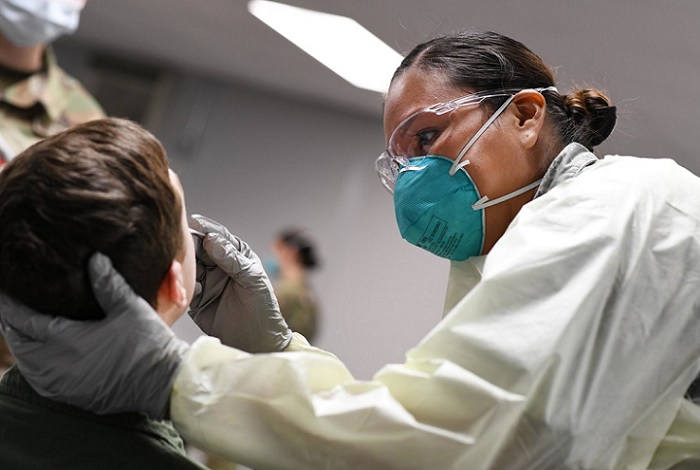
The molecular Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) test detects the virus’s genetic material.
The antigen test detects specific proteins on the surface of the virus.
The RT-PCR nasopharyngeal tests are more widely used and more familiar. Most involve sticking a 6-inch swab deep into your nose to collect virus samples to test. However, some more recently approved RT-PCR tests seek to avoid the discomfort associated with the nasopharyngeal swab tests by allowing samples to be collected via a shallow swab of the nose or by testing saliva for the presence of the virus.
If performed correctly, RT-PCR swab tests “would be pretty close to 100 percent accurate,” says Dr. Emily Volk, an Assistant Professor of Pathology at the University of Texas. To get the most accurate results, RT-PCR tests should be conducted 8 days after suspected exposure or infection, to ensure that enough viral material is present to detect.
Antibody test
As the name suggests, this Covid-19 test look for antibodies made by your immune system in response to an infection with the new corona virus. Antibody tests are not diagnostic tests. Antibodies can take several days or weeks to develop after you have an infection and may stay in your blood for several weeks after recovery. Because of this, antibody tests should not be used to diagnose an active corona virus infection.
Ideally, a positive antibody test would tell you that you’ve recovered from Covid-19 or a corona virus infection and have immunity from future infections, allowing you to return to work, travel, and socialization without the risk of transmitting the infection or becoming sick again yourself. However, researchers don’t yet know whether the presence of antibodies means that you have immunity, whether you could still get sick from a different strain of the virus, or how long immunity lasts.
“Antibody tests are problematic because they can be misused easily,” said Volk. “You may think if you have a positive antibody test that you don’t have to wear a mask or conform to social distancing, but antibodies don’t tell us that you have immunological armor against future infections.” Antibody tests also are subject to false-positive results.
Which test is best?
Experts generally agree that the RT-PCR tests are more accurate and useful than antigen and antibody tests, which are better used as confirmatory tools.



![The Top & Most Popular Seafood Bucket Restaurants in Dubai for you [Never Miss]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/8-seafood-in-a-bucket-scaled-e1600739237403.jpg)
![Procedures for Renewing the Driving License in Abu Dhabi [3 Simple Steps]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Capture-9-e1595666454466.jpg)





