Seafood contains iodine, which is an essential mineral for thyroid health, as it works by helping the body produce thyroid hormones, repair cell damage, control and manage growth, and promote a healthy metabolism.
Unfortunately, a large number of people are at risk of developing a deficiency of this vital mineral. It can be difficult to know if you have this deficiency. As a result, you need to make sure you are aware of the warning signs that may reveal your risk.
Here are nine early signs of iodine deficiency that most people ignore.
Hair loss
Iodine is a substance that the thyroid gland takes from food and turns into hormones called thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones are responsible for many things, including your hair health and subsequent hair loss. Studies have shown that hair loss is a side effect of iodine deficiency, because the thyroid hormones produced by iodine are responsible for:
- Regenerating hair follicles when they die or fall out
- Control of hair follicle growth
- Strengthen hair from the roots
As a result, iodine deficiency leads to:
- Thinning of the scalp and eyebrow
- Decreased hair growth
- Increased hair loss
Therefore, if you find yourself experiencing hair loss, consider this could be a symptom of an iodine deficiency.
Increased feeling of coldness
Some people have low levels of thyroid hormones, which often leads to more sensitivity than usual to cold temperatures. Thyroid hormones are responsible for controlling the speed of an individual’s metabolism. Low thyroid hormones often lead to slower rates of metabolism, resulting in less body heat being produced. Thyroid hormones help in enhancing the formation and activity of brown fat. Brown fat is a type of fat that is primarily aimed at generating heat. Low thyroid hormone levels may prevent brown fat from generating heat, so if you find yourself experiencing cold temperatures often, you may suffer from an iodine deficiency.
Irregular menstruation
Thyroid hormones are also responsible for regulating female reproductive organs and the associated hormones. Research has shown that the vast majority of patients with low thyroid levels will have irregular periods.
Low thyroid hormone levels can disrupt hormonal signals critical to menstrual regulation and heavy bleeding. Fortunately, this problem can be solved simply by consuming iodine in appropriate amounts.
Weakness and fatigue
Do you feel constantly tired and weak? Do you feel as if you do not have enough energy? Iodine deficiency may be the reason for this. Fatigue and exhaustion are two of the most common symptoms of low thyroid levels because they are linked to metabolic rates, which is the conversion of calories into usable energy. So when you have an iodine deficiency, and thus low thyroid hormone levels, the following symptoms result:
- The inability of the body to produce adequate energy.
- A decrease in energy levels.
- Feel helpless
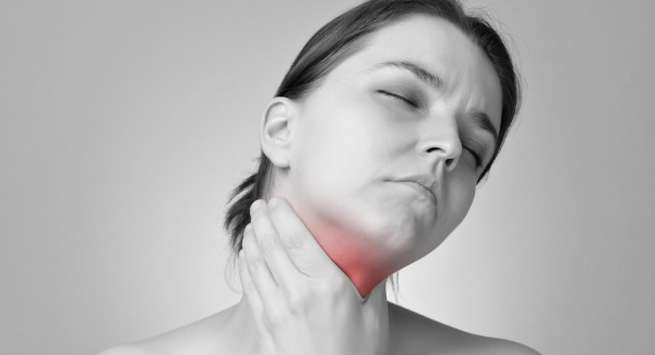
Swelling of the neck
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped organ located at the front of your neck. When you have an iodine deficiency, you may find that the front of your neck swells in response. The thyroid gland will be overworked in an effort to produce the right amount of thyroid hormones. On exhaustion, cells in the thyroid gland will grow and multiply causing swelling and if left untreated, the thyroid gland may grow too large, leading to what is called a goiter. Fortunately, most cases of goitre can be treated with adequate iodine intake.
Decreased focus and productivity
Concentration and productivity require a lot of energy. Since thyroid hormones are essential components of energy production, you may find that you struggle with mental function and work productivity.
Heart rate changes
Thyroid hormones are responsible for a large number of body functions including heart rate. Low levels of iodine often slow the heart rate, and excessive iodine intake increases the heart rate.
Dry skin
It continues to flake no matter how hydrated you are due to the low levels of thyroid gland. The lack of iodine in the body leads to dry, peeling skin. Iodine helps regenerate the skin, regulate sweat, and regulate skin moisture levels, while iodine deficiency prevents the skin from renewing its cells and causes dehydration and the inability to sweat properly.
Sudden weight gain
A common symptom of iodine deficiency is rapid and sudden weight gain. Research has shown that thyroid hormones are a critical component of metabolism regulation. Iodine deficiency lowers thyroid hormone levels and slows metabolic rates. Slow metabolism rates lead to fewer calories burned at rest and lower calories burned means more stored fat.




![The Top & Most Popular Seafood Bucket Restaurants in Dubai for you [Never Miss]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/8-seafood-in-a-bucket-scaled-e1600739237403.jpg)
![Procedures for Renewing the Driving License in Abu Dhabi [3 Simple Steps]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Capture-9-e1595666454466.jpg)





