Brucellosis is a highly infectious bacterial disease, which was reported first in China in the 1970s and 80s. later on, the disease was successfully contained and no more cases were reported until recently. As of September 14th 2020, 21847 people were tested in China, of which more than 3000 people tested positive for Brucellosis. The deadly bacterial outbreak started due to a leak at a biopharmaceutical company last year.
The National Health Commission (NHC) of Lanzhou confirmed that around 3,245 people in the city of Lanzhou, the capital of Gansu province, had been diagnosed with Brucellosis. The infectious disease is usually caused by drinking unpasteurized milk or contact with livestock.
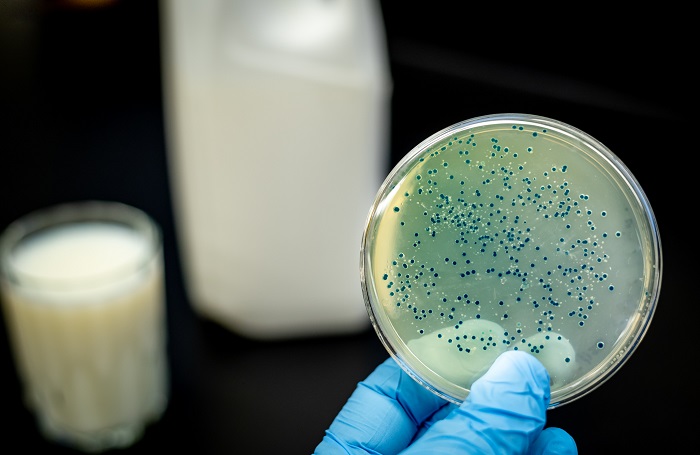
Authorities have now discovered that the Zhongmu Lanzhou biological pharmaceutical factory accidentally vented an aerosolized version of Brucella (the bacteria that causes brucellosis) into the air last summer due to the use of expired sanitizers and disinfectants. The disease can also spread through air or by direct contact with infected animals. However, there is no evidence of human-to-human transmission of the disease yet. Breastfeeding mothers who are infected with the bacteria may still transmit the infection to their infants.
What is Brucellosis?
Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by a group of bacteria belonging to the genus Brucella. It is also known as Malta fever or Mediterranean fever. This bacterial infection affects both animals (sheep, cattle, goats, pigs, and dogs) and humans. It usually spreads due to the consumption of raw or unpasteurized dairy products, direct contact with the fluid of an infected animal or by inhaling contaminated air.
The Brucella species are named as per their primary hosts: B. abortus and B. suis are most common. B. abortus is a pathogen of cattle, B. suis is found majorly in swine whereas B. canis is found in dogs. Also, Brucella melitensis has been spotted in goats, sheep, and camels.

Symptoms of Brucellosis
- Intermittent fever
- Respiratory problems
- Headache
- Abdominal pain, joint and back pain
- Fatigue
- Chills/ Sweats
- Weight /Appetite loss
The infection can affect even other parts of the body – such as the heart, liver, CNS, and the reproductive system. It also leads to infertility in men, arthritis, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), meningitis (inflammation of the membranes around your brain), etc.
Chronic brucellosis can lead to complications in multiple organ systems – skeletal, respiratory tract, liver, heart, gastrointestinal among many others. Symptoms can last for months or even years, but the disease is rarely deadly. However, if not diagnosed, untreated brucellosis has a fatality rate of 5%.
Treatments
Firstly, a doctor tests your blood or bone marrow for the presence of the brucellosis causing bacteria. In case you are severely affected by the disease, you have to go through certain other tests as well. It might include X-rays, CT scans, cerebrospinal culture, and/or echocardiography. The tests are carried out to know the severity of the infection and any other related complications.
As far as the treatment of brucellosis is concerned, the aim is to reduce the symptoms and is usually treated with certain antibiotics. Recovery from the illness may take a few weeks to several months as there is no permanent cure for this disease. Chronic brucellosis is especially hard to cure and causes general fatigue accompanied with persistent fever.
Preventive measures include avoiding raw/unpasteurized dairy products and taking safety precautions by wearing masks, rubber gloves, aprons, when handling animals, or working in a laboratory.




![The Top & Most Popular Seafood Bucket Restaurants in Dubai for you [Never Miss]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/8-seafood-in-a-bucket-scaled-e1600739237403.jpg)
![Procedures for Renewing the Driving License in Abu Dhabi [3 Simple Steps]](https://uae24x7.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Capture-9-e1595666454466.jpg)





